What is international trade? And why does it matter in the world today? In its most basic form, global trade is exchanging goods and services between countries, allowing nations to access resources, products, and innovations that would not otherwise be achievable. It is the result of centuries of history, where, initially, simple barter helped establish what we often see as a complex network for trade when exchanging physical objects on our planet.
How did international trade become so entrenched in the economies of nation-states? Global trade expanded ever faster throughout history, propelled by empires, monetary reforms, technological innovations, and trade agreements. Each transition not only changed economic interdependence but also expanded the geography of trade. From the Silk Road to Ind today, in our Voice and I, each had its own time worldwide.
What are the reasons for studying international trade in an increasingly globalized world? The importance of global trade is undergoing tremendous change, driven by digitalization, sustainability issues, and geopolitical circumstances that affect economies, jobs, and individual lives across the globe. With a basic understanding of international trade, we can see how the history of international trade has shaped the trends that affect and will continue to impact our global economy for years.
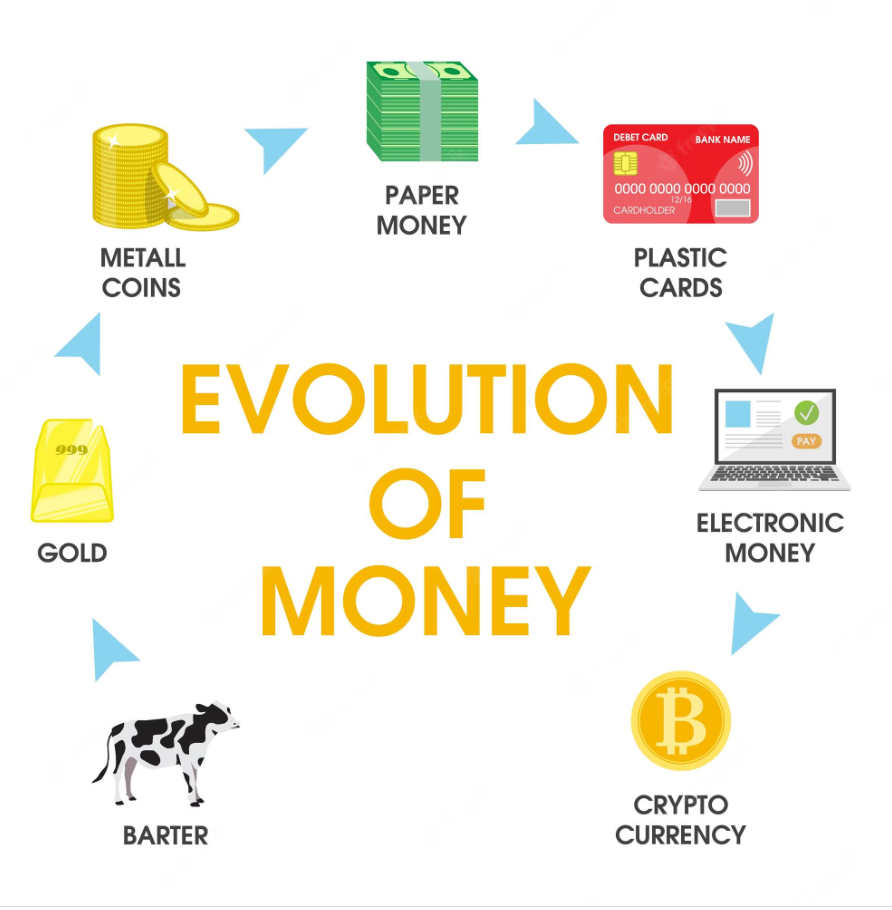
Barter to Money: The Evolution of Trade
The Transition from Barter to Currency
What is the Evolution of trade systems? What motivated humans to shift from essential exchanges of goods and services to more sophisticated trading systems? While ancient cultures traded physical products through barter, the clearly defined needs of this technique naturally made a method for a more accessible exchange based upon fixed values, leading to the standardized currency that significantly changed trade and business.
Silk Road (130 BCE – 1453 CE)
Why was the Silk Road the lifeblood of ancient global trade? Covering 6,400 km and connecting Asia with Europe and Africa, these ancient trade routes and empires facilitated the exchange of silk, spices, ideas, and technologies that defined entire civilizations.
Seas became the highways of antiquity's commerce.
What were the maritime trade routes? The expansion of the Mediterranean, led by the Phoenicians and Egyptians, among other ancient seafaring civilizations, paved the way for global trade and the exchange of ideas.
The spice trade (15th – 17th centuries)
What were Europeans willing to risk a difficult journey for the taste of the East? Many spices, such as pepper, cinnamon, and cloves, were in great demand in Europe, leading to competitive assertions to establish trade routes to Asia. Until 1498, what we now understand as globalization was limited to historical trade routes in the East and West until the Portuguese discovered a new sea route to India. The impact of the spice trade redefined global commerce by enriching European merchants.

The Connection Between Global Empires and Trade Growth
The Age of Exploration (15th – 18th centuries)
What role did European exploration play in changing the course of global trade and empire-building? Motivated by wealth, European countries opened up and set sail to new worlds where colonies would bring about great global trade. The rediscovery of the New World by the time Christopher Columbus sailed in 1492, financed through Spain, began a period of trade—wiping out and forever changing the economic foundation of cultures found in America.
The Atlantic Slave Trade (16th – 19th centuries)
What devastating human costs did the Atlantic Slave Trade impose on global economies? Trade during the age of exploration was driven by the need for a labor force on plantations in Europe; the transatlantic slave trade saw an estimated 12 million Africans transported against their will, irreparably damaging African societies and boosting the wealth of colonial economies through slave labor.
Mercantilism and Colonial Economies
In What Ways Did European Empires Exploit Their Colonies for Profits? Godfrey (2008) argues that at the heart of mercantilist policies, European countries drew resources from colonies, limiting native economic independence and development — fostering dependence. Colonies supplied Europe with raw materials and served as outlets for European manufactured goods, a system that made empires wealthy while impoverishing local economies.
The Connection Between Industrial Growth and Global Markets
18th - 19th centuries
The impact of the Industrial Revolution on trade was a significant milestone in International trade. How did the Industrial Revolution lead to a global demand for resources and markets? Industrial countries, meanwhile, turned to raw materials and new markets to take up the slack of expanding mass production. With the invention of the steam engine, transportation and shipping were again streamlined, as goods could reach faraway markets quickly and effectively.
British Empire and Free Trade Ideals
Why did the British Empire advocate free trade? Britain turned to free trade philosophies characterized, among other things, by the decisive repeal of the Corn Laws in 1846. This enabled the import of low-cost goods, aided in the growth of industries, and positioned Britain perfectly for domination over global trade routes. These were the deep-rooted causes of the British Empire’s free trade policies.
Why Fair Trade Matters in a Globalized World
Post-War Trade Organizations
What is the post-World War II framework for international trade? Countries created organizations such as the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade, or GATT, in 1947 as Post-war trade organizations, which became the World Trade Organization, or WTO, in 1995 to reconstruct and stabilize a global economy. These organizations aimed to reduce trade barriers and encourage a more equitable, free international trading system.
Emergence of MNCs
What made multinationals the main characters in global trade? MNCs’ role in trade grew to serve the world market by lowering costs and accessing different markets. International trade enabled brands such as Coca-Cola and McDonald’s to conquer the world, with products made available globally, resulting in our once-diverse economies falling into each other’s orbits.
Free trade agreements and economic Blocs
How do free trade agreements and economic blocs change the face of international commerce? Trade agreements like NAFTA (USMCA now) and the EU lower tariffs and trade barriers so that goods and services can be exchanged more easily. These partnerships promote integration, enabling growth and competition within member nations.
Six Trends Shaping The Future Of International Trade
E-commerce and Digital Trade Expansion
How does trade evolve with technology? With the massive rise of e-commerce and digital platforms, businesses can now reach customers from all around the globe like never before. Digital trade is driving the turns and twists in international commerce, with projections for monumental cross-border e-commerce growth, making things quicker and more accessible.
Impact of Trade Wars and Geopolitical Tensions
Will trade wars put additional challenges on global markets? Significance of Trade Wars and Geopolitical Tensions Recent examples of trade disputes, such as the U.S.-China trade war, have resulted in tariffs, supply chain disruptions, and rising firm costs. These geopolitical rivalries create risks that can moderate trade growth and destabilize countries dependent on trade prosperity.
Sustainability and Ethical Trade Considerations
Why are sustainable trade practices and ethics? With the ongoing climate crisis, more trade deals will likely include clauses regarding sustainability, carbon emissions, and fair work. This trend promotes responsible business practices that reduce climate impact and establish global ethical standards.
Regional Trade Agreements and Economic Blocks
How are regional trade agreements impacting today’s economy? Free trade areas such as the European Union or the ASEAN Free Trade territories provide member nations with less restrictive trade options to benefit their economies. These deals transform global trade by establishing mega-regional trading blocs and promoting economic integration.
Increased Nearshoring and Reshoring
How are organizations changing their supply chains? Companies are nearsourcing moving production closer to home or resourcing and bringing production back home to reduce reliance on distant suppliers while mitigating risks. Bringing supply chains closer to home is a trend that is altering international trade flows and diminishing dependence on distant shipping.
Automation and AI in Trade
How is automation changing logistics and supply chains? AI, robotics, and blockchain will improve customs, stock and logistics processing, and overall trade efficiencies. These innovations reduce costs, minimize errors, and enable quicker turnaround times, creating a new standard for the global trade landscape.
Recap
What should we know about international trade, and why does it matter for our future? Trade has long been an engine of growth, innovation, and interconnectedness but also a source of challenges, from environmental impacts to hard-to-solve trade disputes. The evolution of international trade and its foundations have given us the knowledge to help us continue adapting to an ever-changing landscape.
What does the future hold for global commerce? Technology, ethics, and how political balances evolve will always shape future trade. Considering historical and current international trade, we position ourselves for a future where equitable, sustainable, and efficient trade can occur.
In an era of historic economic integration, how do we preserve the upside of trade while accepting a commensurate price in futures? Looking ahead, two-way trade practices will remain critical through fair trade, ethical, and innovative trade technology-driven policies that enable a sustainable global economy.


3 Comments
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
**mitolyn reviews**
Mitolyn is a carefully developed, plant-based formula created to help support metabolic efficiency and encourage healthy, lasting weight management.
Quy trình nhận thưởng tại 188V được tối ưu hóa để diễn ra nhanh chóng và chính xác, thể hiện uy tín và năng lực tài chính vững mạnh của nhà cái. TONY01-16